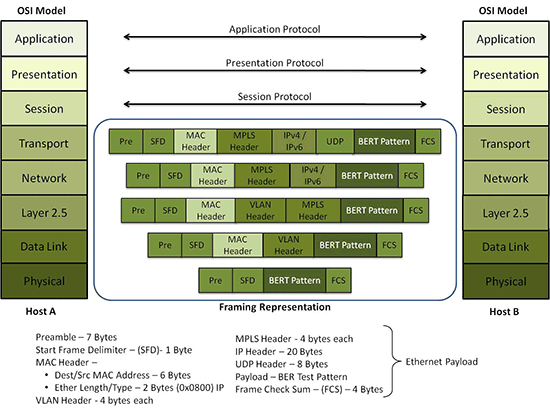
Open System Interconnect (OSI) Reference Model
Nitesh is now
working in a telecom company and wanted to work over a remotely operated machine
which has Linux Operating System. He is working over his laptop which is
windows based and now he is doubted, whether he would be able to telnet the
remote machine. So he asked the same question from his colleague which is
senior to him. His colleague gave him a nod and asked that’s all possible
because of OSI Reference model.
Nitesh is now very
happy and his curiosity starts raises towards the Open System Interconnect (OSI)
Reference Model.
Open System
Interconnect (OSI) Reference Model is a standard defined by International Organization
for Standardization which allows interoperability between different vendors and
helpful in troubleshooting network problems. Various RFC’s has been defined to
for the operation of devices used in various layers of OSI. It has been divided
into seven different layers categorized as:
Upper layers are used to talk to end hosts, these layers performs
programmer specific tasks and
responsible for developing an application. Emails, FTP, TFTP, Telnet,
encryption, decryption of data and authentication of data are all basic
functions of Upper Layers.
Lower Layers are responsible for Network Engineering, which
deals in the delivery of data in a network.
Function of layers of OSI Reference model:
1.
Application Layer: Application layer is
responsible for End host communications. This layer supports all applications
like opening a web page from IE, viewing a video from a vlc media player,
printing a file from a Epson Printer, mail to friend from Yahoo, gmail,
chatting on gtalk or google plus, social media application like facebook,
orkut, etc are all been accessed with the help of Applications layers.
Supported Applications are: Email,
FTP, TFTP, Telnet, SSH, BGP, etc.
2.
Presentation Layer: This layer ensures data can
be understood between end hosts. If we defined it presents the data to Application
layer for representation into desired format. Like if someone send a “.jpeg
image”, presentation layer converts the data of image into EBDIC or ASCII
formation which is computer acceptable and can be transported it to other end
of host which further decrypt with the help of same layer.
This layer is responsible for data
compression, encryption, decryption, decompression functions.
3.
Session Layer: This layer tells how end hosts
figure out whom to talk to, means various end host would be able to talk to
connect the application of their choice. As this layer is responsible for
dialogue control and session control. Let’s take an example of in router we
various sessions has been established, with the help of these sessions we can
control the device.
4.
Transport Layer: The layer develops connection
between sender and receiver and is fully responsible for end to end
connectivity. It divides the data coming from upper layer into smaller segments
and transmits the same into lower layers. This process is called as
Segmentation. This layer provides reliable delivery of data into various
layers, provides error detection and correction. Typical Protocols for OSI
layers are TCP and UDP.
Transmission Control Protocol
(TCP) is a connection oriented protocol provide reliable data delivery .For
example Database Replication from one host to another.
User Datagram Protocol UDP is
connection less protocol provide non-reliable data delivery. For example: video
call or voice progression.
5.
Network Layer: This layer provides connectivity
and path selection, the main function of network layer is Layer3 IP addressing.
The routing of data packets, shortest path selection could takes place over
this layer. The logical addressing of data packets takes place over this layer.
Routers comes into picture at this layer,
Layer3 switches which switches on the basis of IP address are also comes into
this category. The routing protocols responsible are IPv4 and IPv6.
6.
Data Link Layer: This layer defines data for retransmission and
converse of bytes. It also control access to physical media like this layers
tells which media will function first like if we need to access a voice call or
data browsing, data link layer sets the priority and help in accessing the
layers. This layer provides MAC based addressing means on the basis of MAC
address data will travel. Higher order Mac will give lesser priority. This
layer is also responsible for error detection and correction through Cyclic
Redundance Check. Let’s take an example when I put the frame over a copper
cable, if anything goes wrong or any discrepancy occureed at another end, this
layer will publish error on the basis of CRC’s. The devices comes under this
layers are layer 2 switches, bridges, etc.
7.
Physical Layer: All media properties have been
taken care by this layer. The conversion of bytes into computer accepted form
i.e bits are taken place at this layer. This layer controls electrical,
physical data rates, physical connectors, cable distances, optical wavelength
in case of wired media, optical frequency in case of wireless media. The various devices comes under this layer
are Cat5 cable, Fiber Optic cable, Hubs, repeaters, UTP connector, cross
connectors, etc.
To remember the various layers of
OSI reference model, we can memorize as:
All People Seem To be Need Data Processing.
Please Do not touch Steves
Personal Allegator.
Why we use OSI
Layers:
-
For example in application layer, We Server
doesn’t care if Ethernet or wireless was used to reach it. It means if a client
request a web page from the Web Server, it need not to take care about, how the
connection has reached, it will output on the basis of standirds defined in an
application layer.
-
Similarlarly Etherent layer switch wii not care
about IP packets whether they are Ipv4 or IPv6 packets.
-
Like cisco router at one end can talk to Juniper
router at other end.
-
Cisco Switch at one end can communicate to
Netgear Switch at other end.
-
Windows IE browser can connect to Linux Apache
Server.
Encapsulation and Decapsulation
Procedures:
Protocol Data Units (PDU’s) are
the data units which are present at each layer after encapsulating or
decapsulating the data units. It means the final data unit present at each layer are called as PDU’s.
PDU’s at Layer 4 are called as
Segment
At layer 3- Packets
At Layer 2 – Frame
At Layer1- Bits.
The encapsulation process starts
from top layer to bottom layer, means when data units reach at transport layer
a transport layer header and trailer is been added along with the data and it
becomes segments, when going down at Network Layer IP header and trailer has
been added to make it IP Packet. Once it reaches to Data Link layer, it
becomes, frame after adding Ethernet header and trailer. The entire frame is
then further converted into bits and travel over the cable or physical layer
media.
The same process would be taken
care during the process of decapsulation of data reaches moving from bottom to
top..
Transmission Control Protocol/
Internet Protocol TCP/IP:
This reference model was
introduced by Department of Defense (DoD) and basically a condensed model of
OSI Reference Model. It consists of four layers which are equivalent to seven
layer of OSI Reference model.
The four layer model is as under:
·
Application Layer- Equivalent to layer 5-7 of OSI Model.
·
Transport Layer- Equivalent to layer 4.
·
Internet Layer- Equivalent to N/W layer and provide
fragmentation.
·
Network Access Layer- Equivalent to layer
1&2.


Comments
Post a Comment